This component is obsolete and its use in filters is not recommended. Use the recent version of the component.
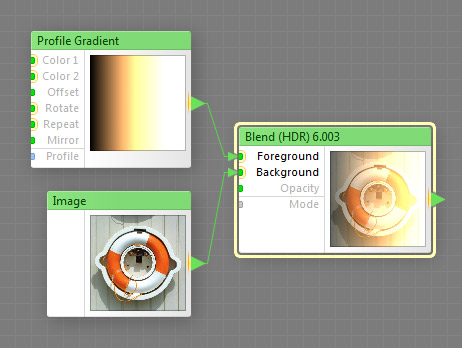
The Blend (HDR) component blends together layers (colors or images) provided by the Foreground and Background inputs, taking into account their alpha channels, the Opacity value and the specified blending mode. This is a map component, it can be located in the Processing category on the Components Bar. This component can output HDR colors. Due to the support of HDR colors the number of blending modes supported by this component is less than that of the Blend component.
Provides the foreground layer which is 'placed' over the background layer. This input can accept HDR colors.
Provides the background layer which is 'placed' underneath the foreground layer. This input can accept HDR colors.
Opacity: Map Input
Defines the opacity of the foreground layer. The value of 0 makes the foreground layer completely invisible. The value of 100 makes the foreground layer fully visible. The actual visibility and look of the foreground layer in the output image are also affected by the selected Mode and the alpha channel of the foreground layer.
Since Opacity is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component. In this case, its output image serves as a mask, where the brightness level defines the opacity: black areas correspond to Opacity of 0, white areas to Opacity of 100, and the opacity values in-between are represented by intermediate brightness levels.
Defines the way the foreground layer is combined with the background layer. The descriptions of the blending modes below assume that Opacity is set to 100 and the alpha channel values for both layers are set to 255 (no transparency):
Normal
This is the default mode. The background layer is completely covered with the foreground layer.
Darken
Compares the values of R, G and B channels for both the foreground and background layers and selects the smaller value for each channel. The three selected values are combined into a color to produce the result.
Multiply
Multiplies the values of R, G and B channels for both the foreground and background layers. The channel values are considered to be in the range of 0 to 1, so the result is darker than both original images. Multiplying any source with black color always produces black, and multiplying with white color produces no effect.
Lighten
Compares the values of R, G and B channels for both the foreground and background layers and selects the greater value for each channel. The three selected values are combined into a color to produce the result.
Linear Dodge
Sums the values of R, G and B channels for both the foreground and background layers. The result is brighter than both original images. Combining any source with black color produces no effect, and combining with white color produces white.
Difference
Shows the difference between the foreground and background layers. If both layers are identical, the result will be completely black. Combining any source with black color produces no effect, and combining with white color inverts the color values of the source. Technically, the result is an absolute value of a channelwise difference between the RGB channel values of both layers.
Hue
Assembles the result from the lightness and saturation of the background layer and the hue of the foreground layer according to the HSY color model.
Saturation
Assembles the result from the lightness and hue of the background layer and the saturation of the foreground layer according to the HSY color model.
Color
Assembles the result from the lightness of the background layer and the hue and saturation of the foreground layer according to the HSY color model.
Luminosity
Assembles the result from the hue and saturation of the background layer and the lightness of the foreground layer according to the HSY color model.