This component is obsolete and its use in filters is not recommended. Use the recent version of the component.
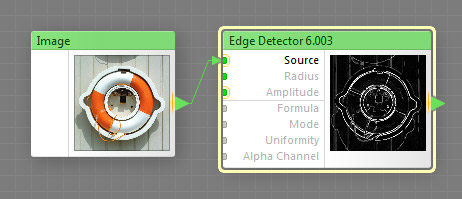
The Edge Detector component detects edges in images using several methods, including the Sobel algorithm. This is a map component, it can be located in the Processing category on the Components Bar. This component can output HDR colors.
Source: Map Input (HDR), Required
Provides the source image. This is a required input – to make Edge Detector work, this input must be connected.
Radius: Map Input
Sets the edge width. Larger values result in thicker, more visible edges. Technically, this input defines the size of the sampling area used for edge detection. Radius is measured as a percentage of the global Size value divided by 40. For example, if Size is set to 600 pixels, and Radius is set to 20, the sampling area will be 3 pixels wide. Since Radius is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Sets the multiplier for the RGB values of the output image. This input is useful for enhancing poorly visible edges the component produces from smooth (low-frequency) source images. Since Amplitude is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component. This input can accept HDR colors.
Determines the detection algorithm: Sobel, Roberts or Gradient.
When set to Grayscale, a grayscale image produced by averaging the source RGB channels is used for edge detection. When set to Channel-wise, the edge detection is performed on each of the source RGB channels separately, and the results are combined to form the output image. When set to Min or Max, the edge detection is performed on each of the source RGB channels separately (similar to the Channel-wise mode), but the output image is grayscale, it is formed by a pixel-wise minimum or maximum of the RGB channels after edge detection. For each mode, the source RGB channels are multiplied by the source alpha channel before processing.
Enhances the edge quality at the cost of rendering speed: None (lowest quality and fast rendering), Coarse (average quality and speed) or Fine (highest quality and slow rendering).
Selects the method for calculating the alpha channel for the output image. When Source is selected, the alpha channel will be taken from the source image; when Average is selected, the alpha channel is calculated by averaging the alpha values of source image samples used for edge detection (which tends to soften the edges in the alpha channel); when Source + Average is selected, the alpha channel will be taken from the source image plus the edge value (which tends to 'thicken' the edges in the alpha channel).