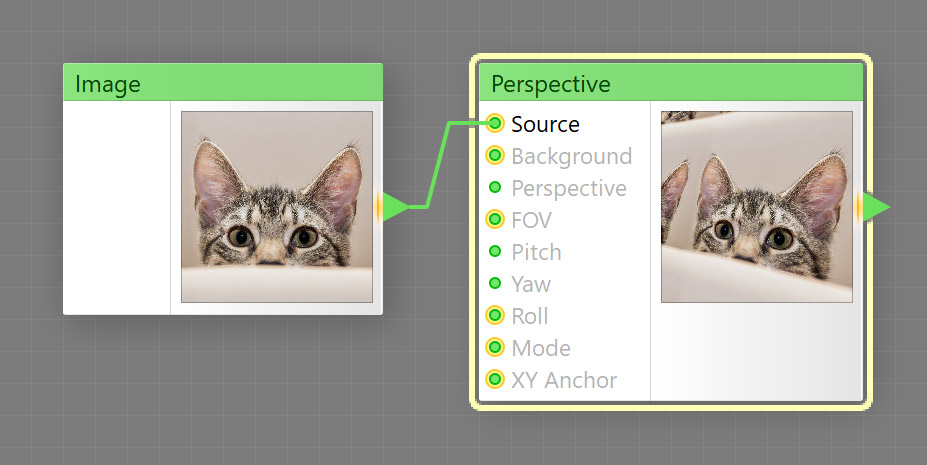
The Perspective component distorts the source image as if it were viewed by a camera looking at the image plane from a specific point. Perspective is a map component, it can be located in the Transform category on the Components Bar. This component can output HDR colors.
Source: Map Input (HDR), Required
Provides the source image. This is a required input – in order to make Perspective work, this input must be connected. This input can accept HDR colors.
Provides the background layer that is 'placed below' the Source image plane. This input can accept HDR colors.
Perspective: Map Input
Defines the distance between the camera and the image plane. When Perspective is set to 0, the point of view is infinitely far from the image plane and no perspective distortion takes place; when Perspective is set to 100, distortion is at maximum level. Since Perspective is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Defines the width of the camera field of view. When FOV is set to 0, the field of view is exactly the same size as the Source image; when set to positive values, it is wider than the image; when set to negative values, it is narrower. Since FOV is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Pitch: Map Input
Defines the camera position along the vertical axis. When Pitch is set to 0, the camera is looking at the image center; when set to positive values, the camera looks 'up'; when set to negative values, the camera looks 'down'. Since Pitch is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Yaw: Map Input
Defines the camera position along the lateral axis. When Yaw is set to 0, the camera is looking at the image center; when set to positive values, the camera looks 'right'; when set to negative values, the camera looks 'left'. Since Yaw is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Defines the camera position along the longitudinal axis. When Roll is set to 0, the camera is looking straight; when set to positive values, the camera 'rotates clockwise'; when set to negative values, the camera 'rotates anticlockwise'. Since Roll is a map input, its value can be controlled separately for different image areas by connecting a map component to this input.
Selects the method to output the distorted image: Clipped, Tiled or Infinite.
The Clipped mode outputs a single copy of the distorted image surrounded by the Background color or image.
The Tiled mode tiles the entire plane with copies of distorted images.
The Infinite mode works well with infinite functions like Perlin Noise: sampling is not limited by the image size and takes place all over the image plane.
When a map component is connected to this input, the number of the selected list item is determined separately for different image areas by the HDR brightness level of the image supplied by that component. The item number is calculated as the brightness level rounded to the nearest integer: the brightness level of 0 to 0.5 corresponds to the first item, the level of 0.5 to 1.5 to the second item, and 1.5 to 2.5 to the third item. Out-of-range values are clipped, which corresponds to the last item of the list.
Determines how the coordinate values supplied by Origin X and Origin Y inputs are interpreted. For more information, see How XY Anchor Works.
When a map component is connected to this input, the number of the selected list item is determined separately for different image areas by the HDR brightness level of the image supplied by that component. The item number is calculated as the brightness level rounded to the nearest integer: the brightness level of 0 to 0.5 corresponds to the first item, the level of 0.5 to 1.5 to the second item, and 1.5 to 2.5 to the third item. Out-of-range values are clipped, which corresponds to the last item of the list.